- cross-posted to:
- usa@ponder.cat
- cross-posted to:
- usa@ponder.cat
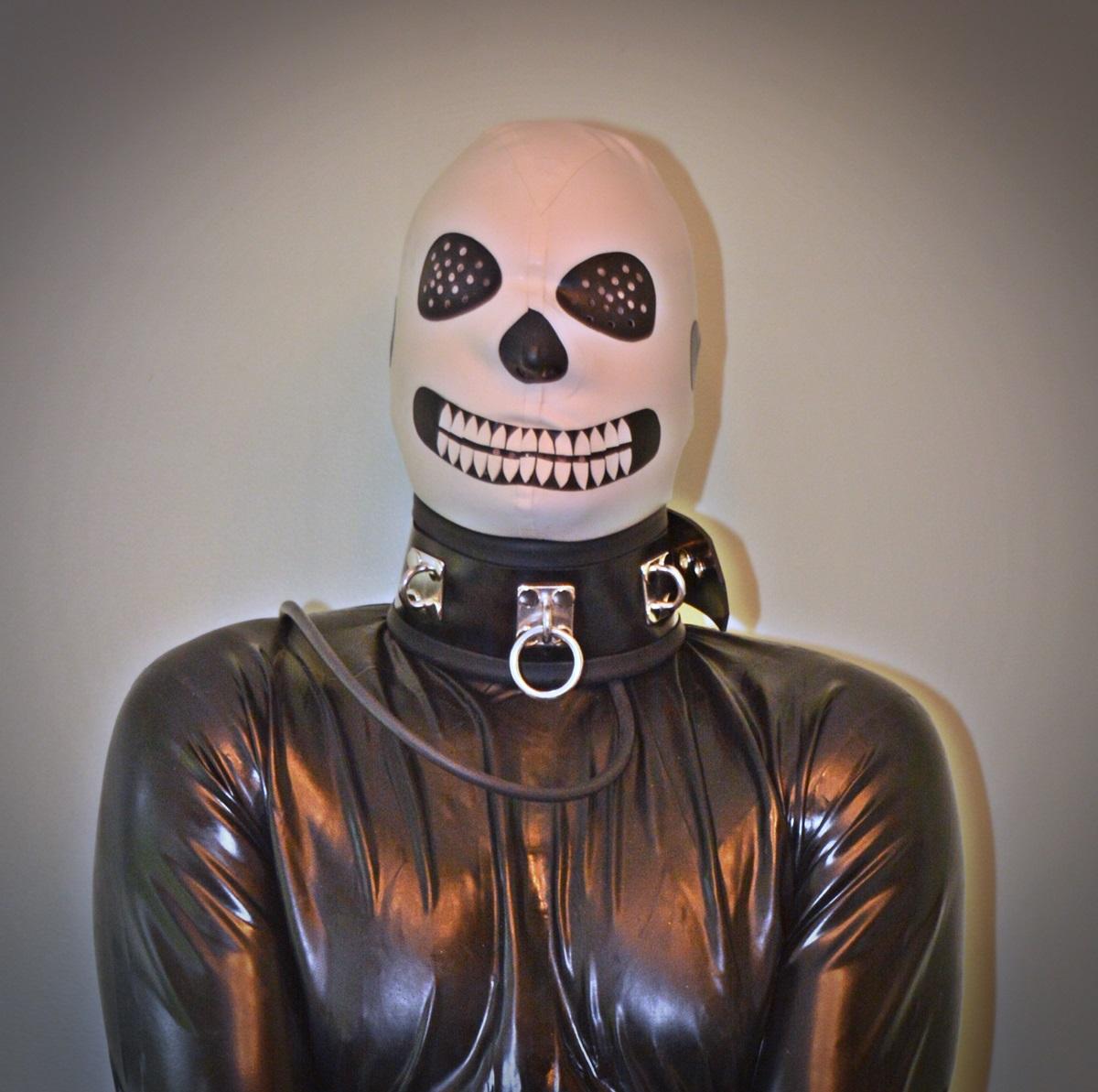
One of the biggest myths about renewable energy is that it isn’t reliable. Sure, the sun sets every night and winds calm down, putting solar panels and turbines to sleep. But when those renewables are humming, they’re providing the grid with electricity and charging banks of batteries, which then supply power at night.
A new study in the journal Renewable Energy that looked at California’s deployment of renewable power highlights just how reliable the future of energy might be. It found that last year, from late winter to early summer, renewables fulfilled 100 percent of the state’s electricity demand for up to 10 hours on 98 of 116 days, a record for California. Not only were there no blackouts during that time, thanks in part to backup battery power, but at their peak the renewables provided up to 162 percent of the grid’s needs — adding extra electricity California could export to neighboring states or use to fill batteries.
California didn’t really debunk anything here. It’s a coastal state with plenty of wind and a predominantly warm, sunny, rain free climate. Of course renewables like wind and solar do well. The reliability concerns are usually more prevalent in areas that have much higher precipitation, and especially in climates that get snow.
From the scientific journal directly sited in the article :
It’s true that solar energy is only produced when the sun is shining on solar panels. Likewise, wind energy is dependent on the ebb and flow of air currents. But the sheer volume of renewable energy being deployed, the ability to store that energy for longer, and to match demand with supply using software, creates a balanced grid.
According to BloombergNEF, lithium-ion battery cell densities have almost tripled, and costs have declined by almost 90% in the past decade – making it easier to smooth out the peaks and troughs of generation to meet the shifts and cycles of demand. Renewable energy sources themselves have dropped by as much as 82% over the same timeframe. Further improvements to both generation and storage will continue driving down costs, making renewable energy even more attractive to consumers.
Ok, but none of that mentions how they plan to account for panels buried under a foot of snow for half the year. That’s the source of the concern, not simply smoothing out daily peaks and valleys.
The article is focusing on California as an example so that doesn’t seem entirely necessary but you could look to Norway to discover how they deal with this:
Vertical Panels are one solution as are Snow Repellent Panels and heated solar panels
Exactly! Like how hydro-power is a dead end and we shouldn’t invest in it.
It’s like, “guys, you know there’s who cities that aren’t by a river, right?”
The snow problem isn’t really that much of a problem if you build for that in mind.
All the panels need is a small heat strip running through some part of it, maybe even behind the panel, added as aftermarket options, to melt it as it falls, and some sort of sensor to only kick heat on when it’s needed. They have things like that for led traffic lights already, so it would really just be repurposing something that already exists.
Sure that uses some electricity, reducing the overall efficiency, but 90+% of the year it’s not actively snowing hard enough to need to kick the heat on, so that’s a minimal loss.
Could even make it a manual thing or periodic and dependent on the panel having reduced power generation during the day. Heat up the snow while the panel is angled and it will eventually fall off without needing to melt all of it. Then, the rest of the time you can just let it get cold.
I wish my car’s wheel wells had that to periodically drop the slush/snow that builds up behind the wheels. Just needs to run for a little bit until the chunk falls off.
I considered mentioning the angled slide-down option, cuz that does work for a lot of applications, but I feel that having it slide off the panel face in a heavy sheet would be bad for it over time, cause scratches and stuff that scatter light and reduce efficiency. Maybe reduce it more than it would be reduced by heating it while it’s snowing heavily, or at least cause it to need replacement or servicing more often.
I’d be more interested to know how things have been in the recent disaster scenarios. The fires have downed power infrastructure all over the place. Have renewables been a positive, negative, or no different in terms of keeping the power on for people?
Shouldn’t be a big change, the transmission system is the same no matter the prime mover.
When fires melted power lines near where I used to live in soCal, SCE would have trucks roll in, dig in new power poles and run the cable. Power restored within about a week, so long as they had stock on transformers.
The grid panels and wind farms are centralized so won’t affect reliability. The house mounted panels will (if your house didn’t catch fire) provide enough energy to run your fridge and house lights.
Right but, for example,
- most solar Inverters require a power supply to operate and define the switching frequency.
- Distributed storage and private generation may have enabled some areas to get by on reduced supply.
- Turbines and solar farms may have been in locations threatened by the fires or been damaged by ash / other debris.
- Repairing grid structure whilst the may be private batteries or generation online (damaged or not) might slow things down for safety reasons.
Once the electrons are on the wires I agree with you, it’s all much the same. However there are other aspects and I expect we’re still learning the good and the bad.
Sheesh I didn’t know the inverters may not run without a grid reference. Where have you seen that, what a terrible idea!
LOL imagine they skimped on a 555 generating 60Hz when in local mode.
As for the rest of your points, this is the kind of evolution we have all had to go through whenever changing something as core as energy distribution. We’ll get better at it.
Where have you seen that, what a terrible idea!
In the user manuals for the inverters I’ve looked at installing. Same is true for many battery inverters.
If they need to integrate with a grid supply at all, they must switch at precisely the right frequency. Mains frequency drifts and so that frequency must come from the grid.
Now some will also have a grid isolated mode where they can generate their own frequency when there’s no other option, but that’s not on all models as it’s a feature they don’t need for 99.99% of their life, especially when grid operators generally don’t want people energising the grid from their batteries when the mains is down as it puts workmen at risk. Cables become live at unexpected times. So if you do have an inverter capable of running without mains you also have to have isolation switch so you only energised your own wiring.
An alternative is a separate isolated output that only ever runs on the generated power and not the mains, but that’s a pain for all the rest of the time.
The systems I’ve interacted with used what’s called an ats, automatic transfer switch, to be sure you’re not energizing the grid so one can self support in an emergency.
I’ve never seen a system so far that wouldn’t run isolated, but maybe I’ve been lucky 🤷
100% for 10/24 hours on 98/116 days is a reeeaaal funky way of doing math
Quite informative really. Its like showing your working out. Tells me a lot more than just the total energy produced.
And a weird way of saying that intermittence is solved…
Exactly. Show me 24 hours on 90% of days then I’m impressed
Ah, yes. Thank you for proving solar and wind are reliable. I’m sure the performance will be completely identical here in Canada where it’s been dim and overcast for the last two weeks and everything is coated in 6 inches of ice and 30 more of snow.
I’m obviously being facetious, but this is a really terrible headline. Renewables have an important place, but using best-case and saying that debunks the idea that they’re unreliable is ridiculous.
Edit: I’m not against renewables, even in colder climates. I’m just mocking the headline itself for its line of logic.
Beyond simply the headline, the first two paragraphs from the article directly address this and site their source ( mentioned quoted above ) which further addresses the issue you are mentioning.
Just as people can get sunburns in overcast skies, solar still works as a net positive energy collection system when scaled correctly. This is why locations with more frequent inclement weather tend to have larger battery stores because even if you only get 0.5kwh from an overcast day, you’re still offsetting that much power use from the grid and over time, it adds up, while the good days help offset the bad days in terms of energy collection so long as you have the storage capabilities.
The primary problem with almost all power systems is how to reliably store as much of that energy as possible given a variable rate of load.
Removed by mod