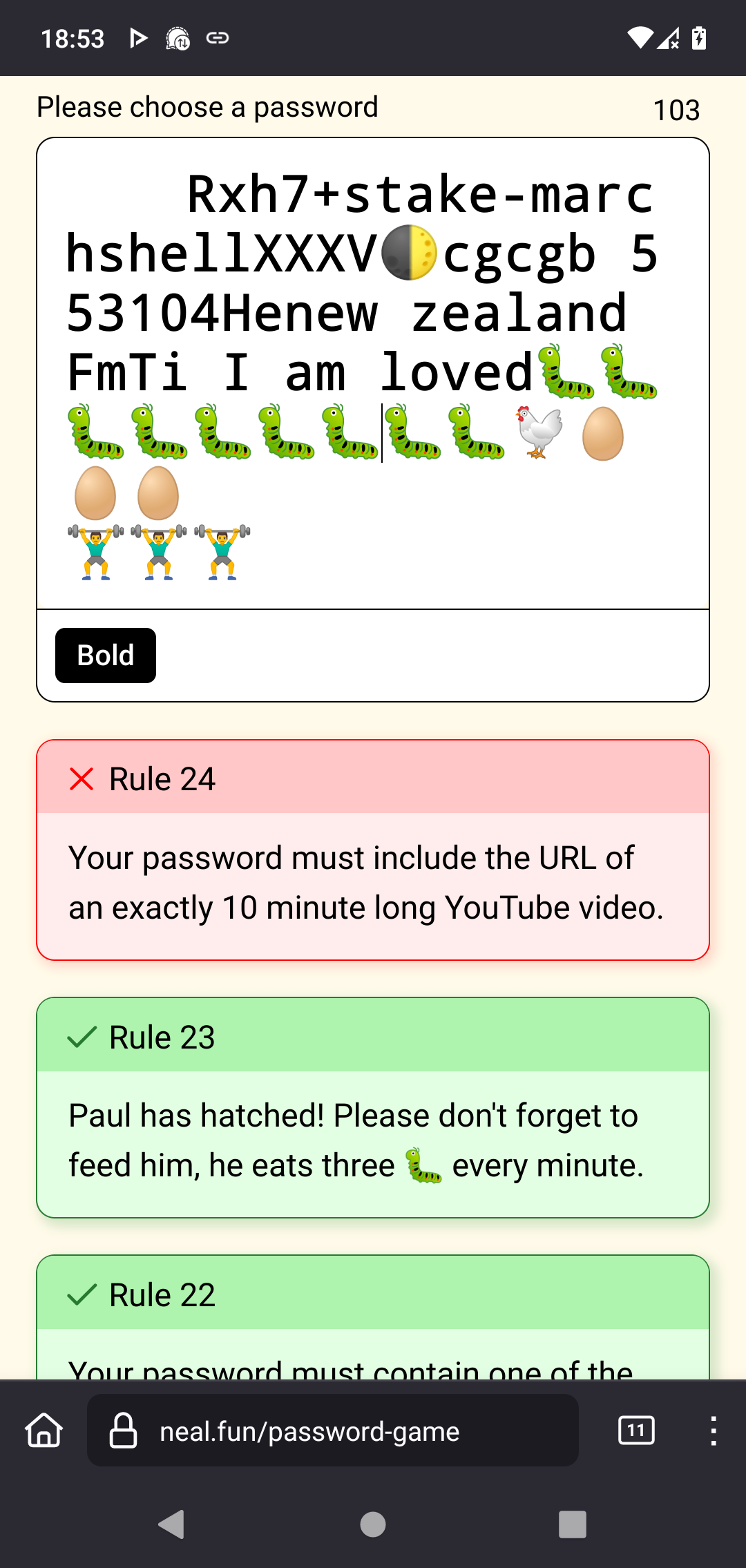
What is your favourite password rule?
My favorite is “can’t be more than x% similar to the last 3 passwords”. Of course, you shouldn’t ever define what “similar” actually means.
And the only way to check that is by storing the previous passwords in a recoverable format.
I’m not sure but I think the previous password is mostly stored in an unrecoverable format and only upon changing your password, when you have to enter your previous one, does it store it in an unrecoverable format for 10x or so generations. Just a guess though for how AD might do it.
That doesn’t make it better.
Even if you only store past passwords, that is absolutely disgusting security practice.
This is everything you ever needed to know about passwords.
There’s a thing called a “one way hash”. It’s a formula run against your plain text password that produces the same result every time it’s run, but can’t be turned back into your password.
Imagine you assign a number for each character, a is 1, b is 2, etc. A (bad) one way hash would be to add up the number of each character and store that. So if your password was “bacj” that would be 2 + 1 + 3 + 10 = 16. So they could store just “16”, but that couldn’t be turned back into your password.
This is a bad hash to use for a couple reasons. One is that many, many things would equal 16. You want something with less overlap or “collisions”. It doesn’t have to be zero collisions either. It’s not completely impossible that more than one password would get you into your GMail, though figuring out which alternative would work would be practically impossible.
The other is that this one is way too fast for a computer to compute. If someone gets your hashed password and the formula they used, they could try a million guesses per minute until they randomly guessed your password. This is called a “brute force attack”. To prevent this, websites use two things. One is that they limit the number of attempts you can make. They can allow you to try ten times per ten minutes and that’s more than enough to slow a brute force attack. But this only stops them if they’re trying through the website. If they have your hash and the formula used on their machine (like a data leak), the attempt limit on the website does nothing. Instead, they should use a “cryptographic hash”, which has all the properties we’ve mentioned, but also takes a good amount of time to compute, even on a good computer. A solid fraction of a second is enough, as long as you used a good password. It doesn’t take many attempts to guess “qwerty” or “shadow” or “misty”, even with leetspeak. If they can guess it in a million attempts, it’s not a good password. Also there are public lists of known passwords that is one of the first things they’ll try.
Another attack is called a “rainbow table”. This is where they take the most common cryptographic hashes, and a list of known, compromised passwords, and they’ll have run the hashes against those passwords years ago and stored them. Now they don’t have to compute the value. They’ll just try each value in the table. To prevent this, every secure site will use what’s known as a “salt”, which is just a random extra password that they’ll literally just stick onto the end of your password before they compute. So even if your password is “shadow”, they’ll have “shadow” + “jfyengighshtogusnwkyifhd” as your password. But the second part is stored in their database in plain text, so the salt is much less secure than your password. You’ll still be vulnerable to a brute force attack, but you won’t be vulnerable to a rainbow table attack.
Remember, if you use the same password everywhere, one site having bad security (or compromised on the front end) means bad actors will have added that password to the list of known passwords. That’s the first thing bad actors will try in a brute force attack forever after. Use a password manager like KeePass or Bitwarden, maybe even 1Password. You have no idea how amazing it is to not need to remember which email you used for which site, and not care what the security requirements are. Every password you have can be 30 character, special character nonsense, and the manager will just handle it for you. I literally can’t tell you my Lemmy password. And I promise that it’s not in that list of known passwords. I just narrowed the possibilities by a few million passwords, does that help you guess my password?
Oh, and getting back to the point, a site can store your past ten hashes without compromising security. It is fucking annoying though.
More modern security practice doesn’t require you to change your password, ever. If there is a required password change, it should be in years, not months. Your good password plus their good security practices means that even if hackers get every piece of data that company has, they still won’t be able to figure out your password for decades, or longer. And that’s only if they try your account first.
(If they take control of the website, they can just read your password when you type it. Another reason to not use the same password everywhere.)
I think you don’t understand the point.
You enter your current password when changing your password. So it’s already there. In memory. There’s no need to persist any plain text.
In memory does not allow you to compare to multiple past passwords.
Stop, they might hear you! “Enter your previous 3 passwords”
I mean, Google already does this for account recovery. One of their recovery methods involves entering “the most recent password you remember” and I’m guessing on the back end also does some precision guess work related to the machine making the reset attempt. If it’s a LG phone in Fargo ND matching one you were previously logged into it’ll be more likely to let you in for example (this is pure speculation based on what I’ve witnessed people struggling to regain access to their Google accounts go through)
My understanding is this is done by saving the hashes and checking the current password against them, and (I’m much less concrete on this one) for “similar” it will run common iterations of the password and save those hashes
At a previous job one of the sysadmins checked all AD users for repeated hashes, and compared against hashes of the top 1000 most common passwords. He also identified one of the IT people had the same hash for both their normal account and their domain admin account, and spoke with them individually to change their domain admin account password
deleted by creator
Or by generating the hashes of all expected permutations of the password the user has just set, and keeping them until the next password is set to compare against. Granted, that would be a prodigious number, but technically doable.
Removed by mod
My personal life? Password manager with passwords as complicated and as long as each service will allow for.
Job that makes me change my password every 30 days? You get the same base password, followed by the next number in the series.
Which is probably why they added the “50% similar” rule. Of course, that just makes the number longer.
I haven’t worked at a company that prevented me from starting over again at my original password after 9 months/resets e.g. password9 reverts back to password0.
If I have to increase the length of my password and make password10, it means they’ve won.
Fuck them.
Of course, if you respect, or even like, the company you work at, you may feel differently.
It feeds your last three passwords into an LLM and it decides if your next password is similar or not. This rule brought to you by Nvidia. Nvidia: the next time your company wants to apply AI to things where AI doesn’t belong, think Nvidia.
This sounds like it could actually be implemented somewhere.
Requirement:
Needs special charactersNot accepted for some reason: using
ọ̵̑h̸̞̉ ̴̰͒g̴͛ͅõ̸̦ḓ̵͠ ̸̳͌w̵̡̛h̴̦͘ŷ̵̫They’re too special.
I like my special little
v̵̂̊̅͌͜ó̶͎̫̜̘̲̭̪̯̔̎̊́̽̒̄̄̕i̸̼̠͓̥̬̙͉͋̿́d̷̨̗̼̖̦͇̲͑̀̈́̔̿̌characters :(Voyager doesn’t like them

Removed by mod
I’m using Voyager too and the unfathomable text isn’t rendering properly either. Voyager version 2.17.0 (Android)

They display correctly for that version of Voyager on iOS.
Removed by mod
I just had to make a password for a hotel.
8 to 20 characters Uppercase Lowercase Digits OR special characters.
The capitalized OR is important. You can have either numbers in the password, or special characters, BUT NOT BOTH.
Took me 8 tries.
- First one was too long.
- Second and third used both numbers and characters, but I thought the characters were TOO special.
- 4 through 6 used both numbers and special characters.
- Seventh password used just letters and numbers, and it was accepted.
- Eighth try I used just letters and keyboard characters, and that was accepted too.
The best part to me is that they include all of these rules to increase the security, but then set a maximum length of the password, which from my understanding is the easiest way to add complexity/security to a password.
The actual funny (or sad) thing about this: even without a length limit all they do is make the password less secure because every constraint just reduces the possible password space.
As someone who generates every password with a password manager those sites are a pain in the ass because you have to somehow get these constraints into the generator.
Keepass deals with this fairly well. It remembers the restrictions from the previous password.
It’s sad that this project from Apple has gotten literally zero traction with any password manager that I know of.
Free, open source repository of password requirements that are just an API call away, and you wouldn’t have to worry about tweaking your password generator at all, but no one is using it. Except maybe Apple and I refuse to use their password manager.
Maximum length is the biggest red flag to me and was the catalyst for me making the effort to switch to unique passwords per-account years ago. There’s just so, so many shitty homerolled security systems out there… and data breaches seem to be a perennial problem these days.
There’s just no excuse for limiting the length if you’re doing security correctly (other than perhaps a large upper limit just to protect against someone DOSing the backend with a bunch of 100MB strings; 512 characters seems reasonable).
By setting an upper limit, you’re basically saying one or more of these things:
- We store your password in plaintext
- We store a hash but our hashing function has an unnecessarily arbitrarily limited input size
- The person/team implementing the backend has no idea what they’re doing and/or just copy pasted login code from stack overflow
- We tried to get away with minimal password requirements but some middle manager wouldn’t rubber stamp it without
arbitrary_list_of_bs
My senior project for uni was replacing the professor’s friend’s website. We had a meeting to gather requirements, have him demo the site as different kinds of users, etc. Dude said “Hold on a sec” and went to a page with all accounts and their passwords listed. Was like, dude, the hell
My ‘favorite’ password rules are incorrect rules. Recently signed up to a service, which looked like it hasn’t been updated since the 90s. They sent me my password via letter, but hey, I was allowed to change it digitally.
So, I did. I set it to a reasonably long password (probably something like 22 characters), with no problems.
Then I went to login and it refused my login. I copied my password out of my password manager, for both setting it and logging in, so there was no way that it was wrong. I quadruple checked the login name, but no luck.
Eventually, I manually typed the password from my password manager. Then I saw it, their password field stopped accepting inputs after about 20 characters.
Presumably, I was able to set my long password on the registration page, but the login page did not accept this long of a password. Fucking ace.
I had to order another password letter.As a website developer, it’s easy to just use the ‘maxlength’ attribute on fields you don’t want to exceed a certain length (for valid reasons or not). But then exactly this happens: A user pastes something in there, doesn’t notice that their input got truncated, and something, somewhere breaks.
‘maxlength’ is terrible user experience.
Yeah, thinking about it now, I could’ve probably tried removing the maxlength attribute to see if the server accepts the longer password.
That doesn’t sound like it should work, but probably would…
That wouldn’t have been (as much of) a problem if the initial password form also truncated the input. The mismatch is the problem.
Let’s say “you wouldn’t have noticed there was a problem if there was no mismatch”. But then a few years later that max length gets dropped or increased and suddenly your password, which has always worked, isn’t accepted anymore, because now you’re pasting 2 extra characters.
I was also not talking about password fields, exclusively. Pasting stuff like customer identifiers or zipcodes into maxlength’d fields also begs for surprises, especially when you can’t see the whole input when you’re done with it.
I understand why stored information, such as passwords, usernames, stuff like that, has to have a max character count.
What I don’t get is why so many people are so daft as to let stuff like this happen, and not even put the maximum password length anywhere people can obviously see it.
If you tell me what the maximum limit is, I’ll be able to keep my password shorter than that.
But no… Password minimum length is shown, symbols, numbers and special character requirements are plainly stated. Maximums? Ha.
Should have right clicked and hit ‘inspect element’ and changed it from 20 to 32487839423 then entered it. Bet it would have worked because, you know HTML hackers.
bonus points for capping the length silently.
I recently made a bit of software that does this. Maximum username and password length of 100 chars can be set, but the login panel only allows you to put 50 chars in the username and password fields. So if you use a password or username longer than 50 chars, youll soft lock yourself out.
But I picked it up in QC testing, it got nowhere near prod. And Im a one man band. I cant fathom how a company could let tgat get past QC.
You can’t? I definitely can.
Got this site once stating “passwords can’t contain parts of username” icw a 64 character pw.
And usenames like “daneelolivaw” block passwords with
da an ne ee el…
dan ane nee eel …
dane anee neel… etc in them
If I was a bad guy and saw this, I would look for users with many different charaters in long names and brute force them, because there’s a high chance they just removed all characters in their names from the pool to generate a password, making it faster to go through the leftover combinations.
Fine, the hacker can see I ordered vegetable vindaloo last Friday. There’s no credit card information stored.
For banks, make your password requirements as hard as you want. For everyone else, I feel like the developers are LARPING as security professionals to make their boring job making web pages for local businesses interesting.
For everyone else, I feel like the developers are LARPING as security professionals to make their boring job making web pages for local businesses interesting.
Wdym my 128 bit password enabled, passkey preferred, https domaines, encryption-within-box standards-meeting secure emailing webserver powered WordPress website for my little kid’s school PTA organization isn’t a viable attack vector? Of course not, you see the web firewall…
Funny you should mention a firewall, a friend who works IT at the county shared how they had to unplug the 911 vendor’s systems from theirs (killing 911 service for the county of course) because they hadn’t updated their firewall for years. They informed the vendor “since you haven’t done your due diligence in updating anything, we are unplugging this. You can figure out the legal ramifications for yourself” so the vendor then flew someone out the next day to update it all
That’s absolutely understandable, since rdaneelolivaw would be the correct username.
That’s what my friend Giskard said. 😁
Always upvote Asimov!
Go ahead. Make a password. Then be left to deal with the mental & emotional damage.
I shared this one with the other IT people at work suggesting we should set it as our new corporate password policy. One of the guys literally finished the game. It took him a week but he did it
Who is he? 😍
For real, though, that’s dedication! Not at all an easy feat. Impressive!
Well, my workplace just announced they’re relocating HQ across the country and bringing basically none of the staff with them, so he’ll be job hunting right about now
Calm down there satan.
“The Roman Numerals…” Is when I gave up.
You didn’t even get to the part where you have to hatch the egg yet? Weak.
played it back when it got viral, that’s when it stopped being fun for me. i was hoping for more rules that would make me think, not for it to become an action game
I couldn’t handle rule 16.
The elements in your password must have atomic numbers that add up to 200.
Seriously?
Edit: I think I lost when my pw got burnt up. Is there more?
Edit2: 3rd try (i think) and I quelled the fire this time. Paul hatched. But: 😒
spoiler
I stopped at wordle. Didn’t want to do anything that required external resources.
I didn’t need an account or anything.
The word was “skate”, btw.
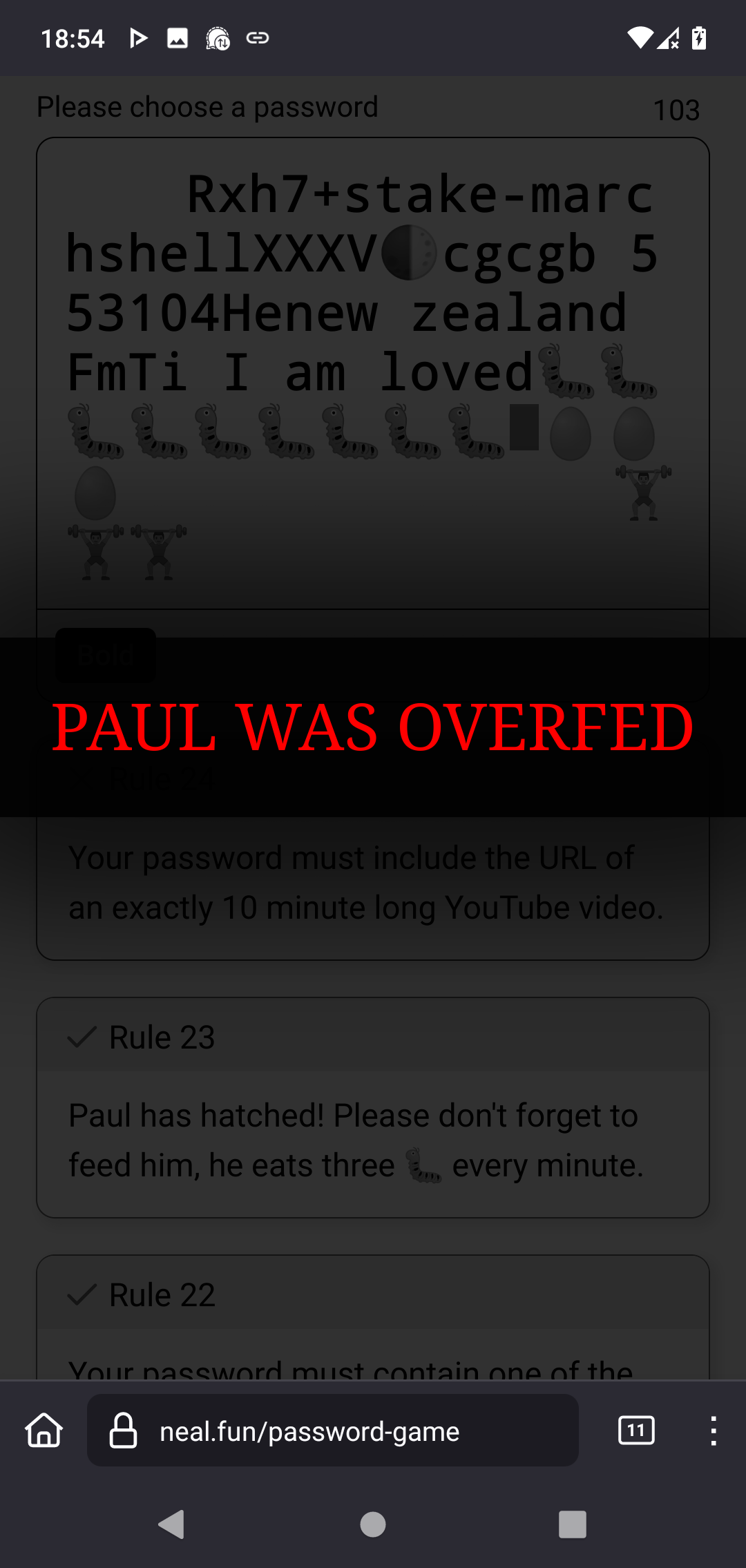
PAUL, NO!!
You got very far, though!
I just wish these password requirements could be added as an attribute to the password field so password managers could generate a password that matches those rules.
I wish we could get rid of many of those stupid rules.
Agreed, but if your password manager can just generate a password that matches the rules, you don’t really have to care about it. Currently you just get your browser/password manager to generate one, get an error, then just manually append whatever missing required character was needed.
But yeah, in most cases the password requirements have not been set by anyone that actually knows anything about password security.
And an implementation by Apple
nowadays we have passkeys anyways which is just making the good old “random max length password with all the character groups” explicit.
One that I loved was that you couldn’t set any from a list of “common passwords”… You couldn’t include anything from that list in any password you used. So if the list included the word “green” then “3875429$##&!32++_@greenbean2284&$@” would be rejected.
What’s on the list? (Shrugs)
Good luck!
“Sorry, this password is too long”
Literally gotten this error before. So annoying. It was like 18 characters.
That could either mean they want to limit DDOS traffic caused by absurd long passwords, but unlikely.
Or they store your passwords in plain text instead of a proper hash value in their way to small fields in database.A more absurd possibility would be if they limit characters because they send the form by GET instead of POST and everybody could see your password in the URL (e.g. in all logs).
Security nightmare in any case.I had one site limit my password to 8 characters long
That’s the worst. I already made a meme about it last week.
I’m sorry, but passwords must be unique across the entire platform. The one you entered matches johnDoh@xyz.dev. Please try again.
Password requirements so secure, eventually you go full circle to remember them and do shit like this.
Expires every X months.
I’ve never been super into the idea of using a password manager rather than just using complex but memorable passwords for everything, but policy like this basically necessitates using one.
Unless it’s the one password you actually use to login. I can’t use a password manager for my Windows login.
Most people I’ve met simply use the same password and increment one number somewhere.
Or several numbers if it can’t be too similar to a previous password.
The internet banking portal for one of my banks forces a monthly password reset. As a result it is the only bank account for which i have the password saved in my browser, instead of being a nice long memorable phrase that lives only in my head.
The good old NTLM rule of max 8 characters and all converted to uppercase. It was a simple rule and if you forgot your password you could easily bruteforce it with normal consumer hardware.
at what point do password requirements start making password easier to crack?
They already do. If I know a number is required, I don’t have to try any passwords that don’t have a number.
They invariably do. They always constrain the list of things that a fully random generator could possibly make. They never add to that list.
Even rules like “can’t use the same character twice in a row” constrain the list at least a little. That one makes it harder for dumb people to do dumb things, but also makes it harder for smart people to do smart things.