In this study, the scientists simulated the process of spaced learning by examining two types of non-brain human cells — one from nerve tissue and one from kidney tissue — in a laboratory setting.
These cells were exposed to varying patterns of chemical signals, akin to the exposure of brain cells to neurotransmitter patterns when we learn new information.
The intriguing part? These non-brain cells also switched on a “memory gene” – the same gene that brain cells activate when they detect information patterns and reorganize their connections to form memories.
Memory is stored in the balls
Just to recap, sperm, pee, microplastics, and memories are stored in the balls? Am I missing anything? I can’t remember. Maybe my balls are too full of microplastics to recall.
Data.

I’m sure you could fit a few dollars in loose change in there to.
I keep cement in mine
Mine are filled with brass
Live bees here
Yukon gold potatoes.
You forgot about the wolves.
i forgot i put those there to control the deer population
The Soul is also stored in the balls.
Do you think that’s why we often tell god that we’re cumming?
Urine is not stored in the balls. I’m a doctor you can trust me on this
Even if you weren’t a doctor I’d agree with you. I was taught it’s stored in the bladder in ninth grade. Pretty sure that continues throughout your adult life. Lol
I thought you were referencing the conversation on Reddit or Twitter or something where someone had said “I’m a doctor, pee is definitely not stored in the balls” and then a really long argument ensued where the dude was pretty adamant that pee is stored in the balls. I just wanted to be the Dr
deleted by creator
And when you fuck someone, you’re giving them your memories.
Vaginas remember the bad balls.
And if they swallow a load….
I think you may have just figured out alzheimers. You can’t go nutting away all of your memories.
Still better that “pee is stored in the brain”
Well some species do potentially have “genetic memories” so maybe some stuff actually could be
😆
in a laboratory setting.
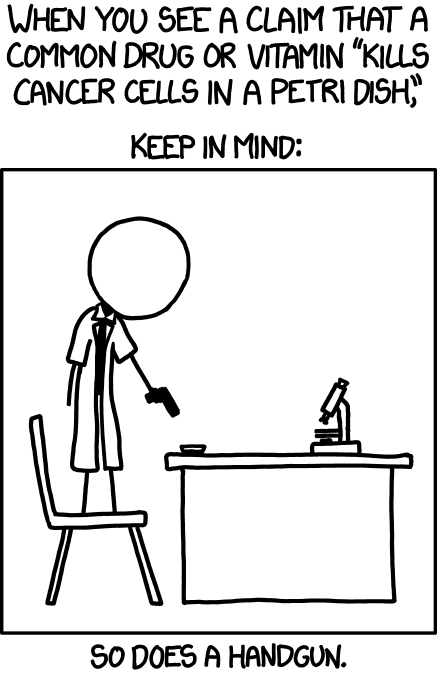

Technically, a handgun also kills cancer in vivo. The problem is the cost to the host body.
Okay but what you’re saying is if I hired a good enough marksman to shoot the cancer out of my body without killing me then that’s a good thing right?
I mean, that’s basically what we do with gamma radiation and chemotherapy, just a little bit more ballistic, right?
Exactly! The only difference is that those use very tiny bullets.
Chemo only applies if it’s doped with a radionuclide, otherwise it’s just regular poison.
Do we need to format our kidneys before becoming a donor now?
Maybe. There are numerous reports of people having changes in personality after organ transplants.
Personality changes following heart transplantation: The role of cellular memory https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31739081/
https://www.sciencealert.com/eerie-personality-changes-sometimes-happen-after-organ-transplants
Damn, that’s interesting!
To be fair, I think anyone going through something as traumatic as basically being put into stasis and having their heart cut out and and then having one reattached would change a bit simply because of the process.
I mean, you don’t keep stepping on Lego bricks barefoot after you’ve done so, and we expect people who have had a heart ripped out and then another one reinserted to act the same?..
Many stories like this from fecal exchanges (trans-poo-sions)
Yes, that is also true. Many things make up the mind, and changing a major input, e.g. the microbiota that make a particular mix of short chain fatty acids and other neuro effective compounds, is going to change the cognitive outputs.
You really should affix the possible reasoning to your comment up the chain
changing a major input, e.g. the microbiota that make a particular mix of short chain fatty acids and other neuro effective compounds, is going to change the cognitive outputs.
This post is wildly running into speculation and I fear several users are taking the wrong implications that “conscious memory” is scientifically being validated as stored in the bodies several organs.
Not to be a debbie downer here, but it’s important to keep in mind that unless expressly stated otherwise, so-called discoveries that are only published in out-of-the-way (ie. not respected scientific journals) have usually not been peer reviewed or had their results replicated, which is the entire point of the scientific method.
Here’s the paper.
Awesome. Thanks!
Its not the same memory as your brain. your life story is not in your non nerve cells. they have memory the same as yeast has memory but everyone is aware of how we have muscle memory in reptitive tasks.
I think muscle memory is just a phrase, but the training that makes and embed the “muscle memory” is essentially nural
yeah sorry I still feel that is neural just not all the way to the brain. I guess what I was trying to say if the article is not that cells hold your memory but that they hold their type of memories is a similar way.
Its interestng, but kidney cells are not exposed to patterns of neurotransmiters like nerve cells are. Cells can be reprogramed to be stem cells as well with the right pattern od signals but that does not mean that it really happens in the body.
fascinating, this concept is a core to the theravadan buddhist practice of vipassana meditation, which is supposed to be what the buddha himself actually taught in his wandering classroom. I always took that bit with a grain of salt assuming it was just an old misunderstanding of what’s going on but the kind of non-thought memories appears to be exactly what is described.
it’s called Vasana and it’s said to be like ‘perfume lingering in cloth’, the residual karma from our actions that shapes our future and influences automatic actions and preferences. Trauma is said to be stored in the body as well as Sankhara.
I have always viewed vipassana as mental martial arts more than religion, and brushed off all the reincarnation and other inexplicable stuff. fascinating to hear scientists confirming what philosophers came up with thousands of years ago.
There are many stories on how the receiver of a transplant has felt themselves being “changed”, sometimes in ways that would remind people of the donor.
MDPI is like the lowest quality slop journal. Like anything gets peer reviewed in that thing.
Isn’t the title misleading? A cell switching on the same gen neurons use to connect, if exposed to substance used to transmit information, doesn’t mean it stores or transmits any memories. It seems it doesn’t even do anything more, like forming dendrites or “answering” chemically.
Guess that’s just a side-effect of how the gen is exposed.
It’s more than that. People who have had heart transplants can inherit memories and personality traits from the donor. Cells remember more than they let on and can pass these memories to the recipient.
See this study. I think it’s safe to say we have some empirical evidence for this. In the linked study, there’s a kid who received a heart from another kid who died trying to retrieve a power ranger and somehow the donor knew that without anyone telling him. Another kid received a heart from a kid who drowned and he became afraid of water.
If I read the cited sources and they turn out to be a bunch of untested hypotheses based on poorly conducted studies… I’ll be mad.
Just skimming through it makes a bad first impression.
…I’m not even trying to be derisive. I’m just really angry at how much “there’s a study” has become “there’s proof”. And I shouldn’t even be mad because communicating that difference should be the authors’ job.
If you value your time, don’t read any further because I’m just going to vent a little:
So I lack any formal education (apart from ficking school). The best thing I can say about myself is that I can hold and mostly understand a conversation with people who are actually educated in their field.
But some studies are bad. Like bad-bad. So bad that I think, most people who can read should be able to recognize their flaws if they actually read them.
For example:
I read a study a while back about genetic (as opposed to learned) prepositions of monkeys in relation to their biological sex and preference for toys.
The methodology was bad, but here’s the shittiest part imo: At the end of the study, the researchers found that of the 130 or so monkeys, only about half showed any preference for any kind toy. So the researchers excluded the unbiased monkeys from the test. Of the remaining monkeys, still only the males showed any preference for the “male” toys. So the females were also excluded. In the end, only 30 monkeys actually counted, because they showed the hypothesized difference in their preferences. And even those only showed a delta of 10-30% in the time they spent with the toys.
The study should have concluded that most monkeys don’t give a shit if a toy has wheels (like a shopping cart, which apparently makes it a “male” toy) or if it’s soft, like a plush (which is “female” because boys would never touch a plushy, of course).
Instead, they found that their hypothesis turned out to be correct, after disregarding anything that invalidated their hypothesis.
Where did I get this study from? From social media, of course. Where a bunch of meat heads “proved” that all women genetically want to be tradwives and trans people don’t exist or some shit.
Fuck everything about this.
Sounds like utter bullshit to be honest with you.
At the bottom of that article you linked:
“Research data for this article Data not available / No data was used for the research described in the article”I’m all for implications but I think a little higher level of standards should be practiced since this is c/science.
The title is “misleading” because they’re not talking about visual/conscious mind memory as you’re doing here.
These non-brain cells also switched on a “memory gene” – the same gene that brain cells activate when they detect information patterns and reorganize their connections to form memories… "it suggests that in the future, we will need to treat our body more like the brain — for example, consider what our pancreas remembers about the pattern of our past meals to maintain healthy levels of blood glucose or consider what a cancer cell remembers about the pattern of chemotherapy.”
Furthermore, you’ve jumped onto anecdotal evidence and have declared it Empirical with your linked study
A literature review was performed to explore accounts of personality changes following heart transplantation … Further research is recommended.
That level of evidence would mean anyone claiming body transfers, alien abductions, past lives memories, etc etc would all be empirical data we must now scientifically accept.
I don’t see how you’re linking the two studies with the implied “It’s more than that”. The original study from OP is declaring nothing about actual memories that we’re “consciously using” being stored in other parts of the body. It’s stating they believe cells have “memory mechanisms” to better function, like a processor getting it’s own memory cache (that data storage is used for it’s processing purpose and isn’t included with your harddrive access).
They are a little deceiving/misleading with the article as well,
The goal of the research was straightforward — to investigate if non-brain cells contribute to memory… They ingeniously engineered the non-brain cells to generate a glowing protein, which indicated whether the memory gene was active or dormant… Not only does this research on non-brain cells introduce fresh perspectives to study memory, but it also holds promise for potential health-related benefits.
They tested a gene by bombarding cells with chemical cocktails, showing the gene can be activated. It’s a giant leap to then say we have empirical data that we store memories throughout our bodies.
Its like the blockchain for you body.
I am become nft
Identifier of ownership
“The Body Keeps the Score”
“Muscle memory” is real.
Yeah last week people on Lemmy were arguing that memory is the simplest thing to exist EVER and that musk’s neuralink meant we had matrix reloaded already at the corner
The hubris never ceases to amaze me
Musk is a snake oil salesman that buys other people’s ideas and pays smart people to make it, then steals all the profits for himself.
Modern day Thomas Edison.
Except he hasn’t electrocuted a live elephant to make a point. Yet.
In related news:
The complications include bloody diarrhea, partial paralysis, and cerebral edema, a condition colloquially known as “brain swelling.”
It seem like they’re just saying kidneys remember kidney stuff, pancreases just remember pancreas stuff, etc etc.
It’s not like your kidney remembers Aunt Jean has a mole on her nose.
There is another body of research that deals with a person’s behavior can be heavily influence by endocrine actions. Organs can affect current endocrine responses. So there is a suggestion here that your kidney may not remember the Aunt Jean has a mole, it may remember why it releases certain hormones which can effect how you behave.
Yeah, but if you get someone else’s kidney, it “remembers” how that body worked.
I dunno. We (both my wife and I) can and have had long conversations with my gut (when there’s a rumbly in my tumbly you can hear it across a crowded room) and my gut seems to remember shit. It also has a strange fascination with cheese.
That sounds like a fun life/wife.
I am a very lucky person, and she is. It’s kind of like when you have a conversation with your meowbox of an orange tabby.
So hold on a minute - does this mean there might be some truth to the whole “eat your fallen enemy to gain experience” thing? That’s wild.
naw. its more like the nerve pathways through the body also have their own node-weighting long before they get to the brain. those are used in process sometimes allowing for memory-like function
its still a generated system that you cant just eat
Closer to that whole organ transplant affecting someone’s personality I guess
Eating a dictionary to improve your vocabulary would be equally effective to that theory, and for many of the same reasons. (As far as information transfer is concerned)
No, because you’re eating the flesh, so you’re digesting it.
This is more relevant to organ transplants.
Apparently, it’s a known phenomenon that some organ transplant recipients seem to inherit some traits and even memories of organ donors.
Wow, these examples are so cool.
Food Preferences:
- developed aversion to meat after receiving a heart from a vegetarian donor.
- experienced nausea after meals post-transplant from a donor with irregular eating habits.
- developed a taste for green peppers and chicken nuggets, foods favored by her donor.
Musical Preferences:
- began enjoying loud music post-transplant.
- developed a love for music after receiving a heart from a musician.
- started appreciating classical music, previously disliked, after transplant.
Sexual Preferences:
- Male recipient of a heart from a lesbian artist experienced heightened desire toward women.
- Lesbian recipient of a heterosexual woman’s heart found attraction to men.
Other Preferences and Aversions:
- Landscape artist’s heart recipient developed interest in art.
- Dancer’s heart recipient shifted color preferences to cooler tones.
- Fear of water developed post-transplant from drowning victim.
Memories:
- describes sudden unusual tastes accompanied by thoughts about their donor’s identity and life experiences.
- feels tactile sensations corresponding to the impact of the car accident that killed their donor.
- experiencing flashes of light and heat resembling the trauma suffered by their donor, who was shot in the face.
- describes a vivid dream of reckless driving, mirroring the circumstances of their donor’s fatal motorcycle accident.
Some recipients even experience dreams or memories aligning with their donor’s identity, such as a woman envisioning a young man named Tim during a dream and later discovering her donor’s name as Tim Lamirande
Unfortunately, though, I don’t see any mention of how certain they were that the recipients didn’t learn these things before experiencing them